Arginase-1 Antibody – 150Nd
Isotype: Rabbit IgG
Reactivity: Human*
Application: MIBI-FFPE
Storage: Supplied in antibody stabilizer with 0.05% sodium azide. Store at 4°C.
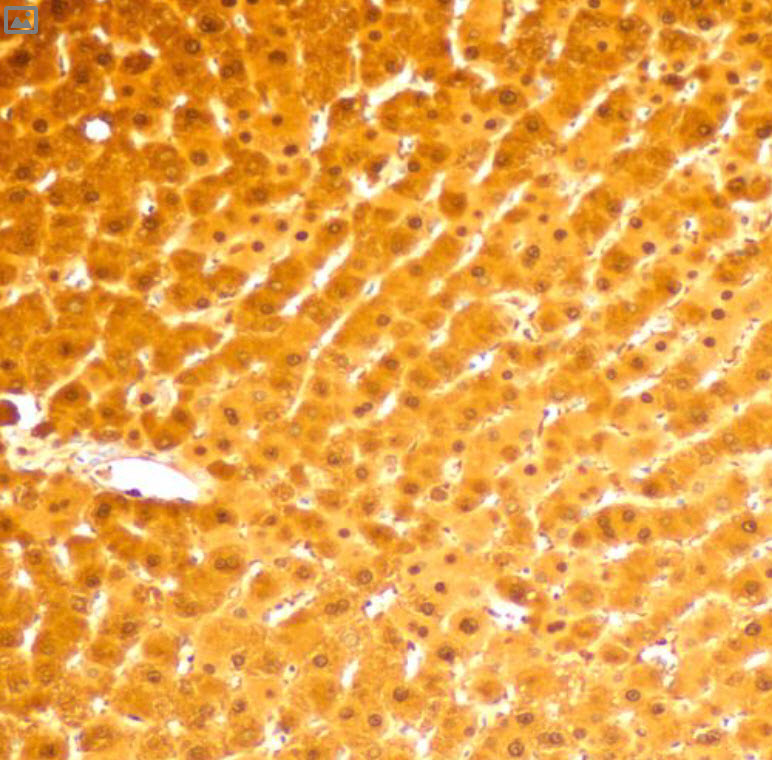
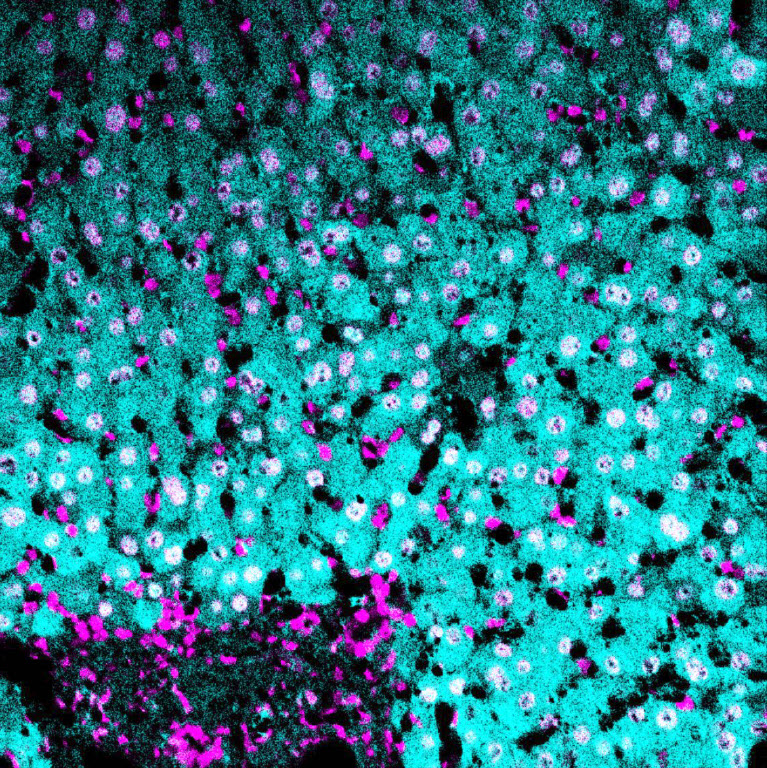
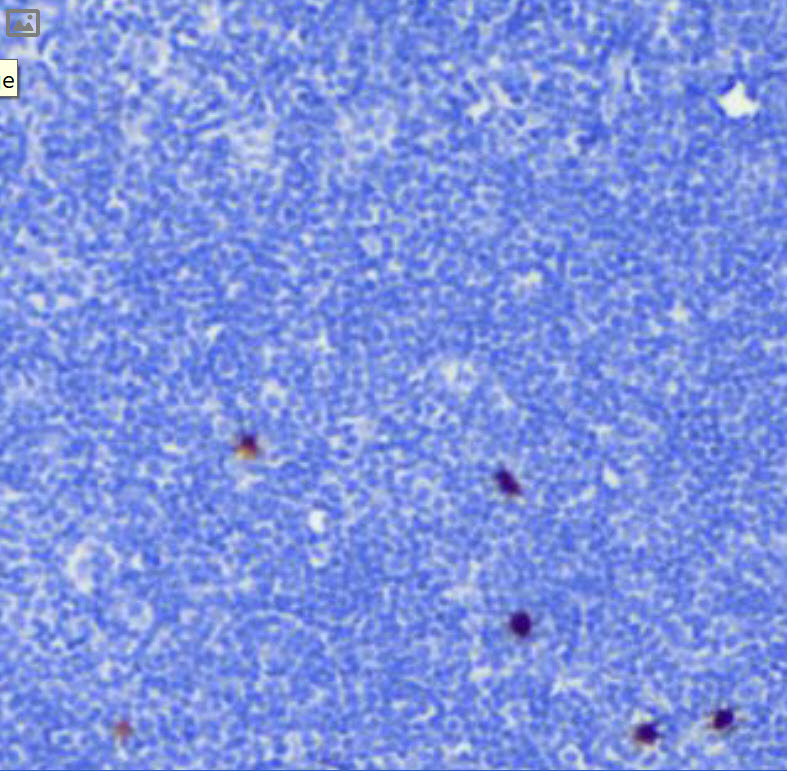
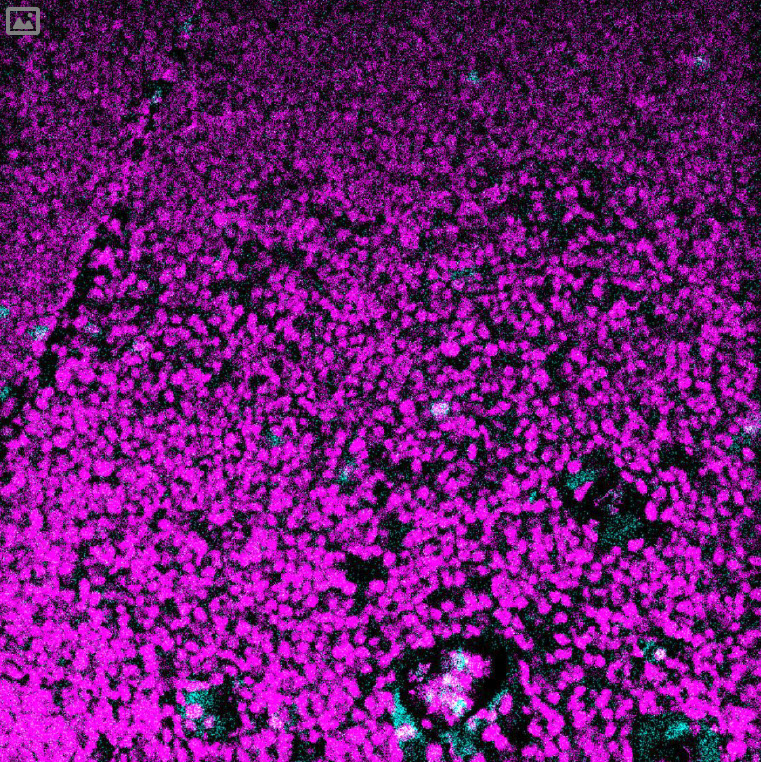
(cyan) of FFPE human thymus, counterstained with Histone H3 (magenta)
Validation: Each lot of conjugated antibody is quality control tested by staining tissue following the MIBI Staining Protocol optimized for the applicable tissue format with subsequent MIBIscope analysis using the appropriate positive and negative tissue field of views. These results are pathologist verified.
Recommended Usage: Human FFPE: 1:100 dilution. For optimal results, the antibody should be titrated for each desired application.
MIBI technology: Learn more about MIBI™ Technology, a multiplex IHC technology with unmatched sensitivity and true subcellular resolution.
References
- Rodríguez, P.C., Ochoa A.C. Arginine regulation by myeloid derived suppressor cells and tolerance in cancer: mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Immunol Rev. 2008; 222:180-91.
- McGaha T.L. et al. Amino acid catabolism: a pivotal regulator of innate and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev. 2012; 249(1):135-57.
* Conjugate tested on human and mouse FFPE tissue.